COLON CANCER: CAUSES, SYMPTOMS, AND TREATMENTS

1. What is colon cancer?
Colon cancer forms when this uncontrolled cell growth happens in the cells of the large intestine. Most colon cancers originate from small, noncancerous (benign) tumors called adenomatous polyps that form on the inner walls of the large intestine. Some of these polyps may grow into malignant colon cancers over time if they are not removed during colonoscopy - a procedure looking at the inner lining of the intestine. Colon cancer cells will invade and damage healthy tissue that is near the tumor, causing many complications. After malignant tumors form, the cancerous cells may travel through the blood and lymph systems, spreading to other parts of the body. These cancer cells can grow in several places, invading and destroying other healthy tissues throughout the body. This process is called metastasis, and the result is a more serious condition that is very difficult to treat.
Colon cancer is not necessarily the same as rectal cancer, but they often occur together in what is called colorectal cancer. Rectal cancer originates in the rectum, which is the last several inches of the large intestine, closest to the anus. According to the American Cancer Society, there will be 95,270 new cases of colon cancer in the U.S. in 2016.
2. Causes of colon cancer
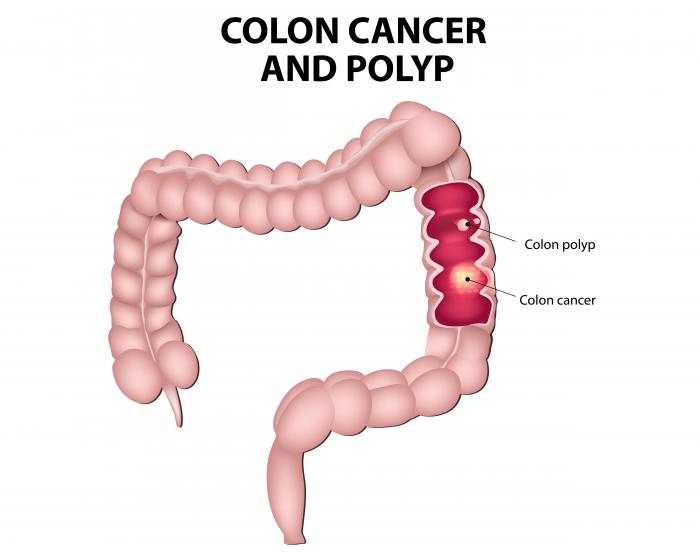
Normal cells in the body follow an orderly path of growth, division, and death. Cancer is ultimately the result of cells that uncontrollably grow and do not die. Programmed cell death is called apoptosis, and when this process breaks down cancer results. Colon cancer cells do not die in the normal way, but instead, continue to grow and divide. Although scientists do not know exactly what causes these cells to behave this way, they have identified several potential risk factors:
Polyps
Colon cancer usually derives from precancerous polyps that exist in the large intestine. The most common types of polyps are:
- Adenomas: can become cancerous but are usually removed during colonoscopy
- Hyperplastic polyps: rarely become colon cancer
- Inflammatory polyps: usually occur after inflammation of the colon (colitis) and may become cancerous
Genes - the DNA type
Cells can experience uncontrolled growth if there is damage or mutations to DNA, and therefore, damage to the genes involved in cell division. Cancer occurs when a cell's gene mutations make the cell unable to correct DNA damage and unable to commit suicide. Similarly, cancer is a result of mutations that inhibit certain gene functions, leading to uncontrollable cell growth.
Genes - the family type
Cancer can be the result of a genetic predisposition that is inherited from family members. It is possible to be born with certain genetic mutations or a fault in a gene that makes one statistically more likely to develop cancer later in life.
Traits, habits, and diet
Age is an important risk factor for colon cancer; around 90 percent of those diagnosed are over 50. Colon cancers are more likely to occur in people with sedentary lifestyles, obese people, and those who smoke tobacco.
Diet is an important factor associated with colon cancer. Diets that are low in fiber and high in fat, calories, and red meat and processed meats increase the risk of developing colon cancer.
In fact, Western diets increase the risk of colon cancer compared with diets found in developing countries. Heavy alcohol consumption may also increase the risk of colon cancer. Being overweight and physically inactive are also risk factors for developing colon cancer.
Other medical factors
There are several diseases and conditions that have been associated with an increased risk of colon cancer. Diabetes, acromegaly (a growth hormone disorder), radiation treatment for other cancers, ulcerative colitis, and Crohn's disease all increase the risk of colon cancer.
3. Symptoms of colon cancer
Cancer symptoms are quite varied and depend on where the cancer is located, where it has spread, and how big the tumor is. It is common for people with colon cancer to experience no symptoms in the earliest stages of the disease. However, when the cancer grows, symptoms include Diarrhea or constipation, Changes in stool consistency, Narrow stools, Rectal bleeding or blood in the stool, Pain, cramps, or gas in the abdomen, Pain during bowel movements, Continual urges to defecate, Weakness or fatigue, Unexplained weight loss, Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS),

Iron deficiency (anemia).
If the cancer spreads, or metastasizes, additional symptoms can present themselves in the newly affected area. Symptoms of metastasis ultimately depend on the location to which the cancer has spread, and the liver is the most common place of metastasis.
4. Prevention of colon cancer
Colon cancer is the third most common cause of cancer death in the U.S., and it is the second most prevalent type of cancer. Regular annual screening for both men and women aged 50 to 75 years is recommended by the U.S. Preventive Task Force.
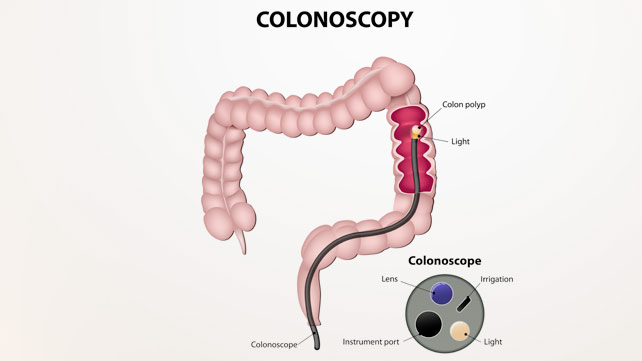
The American Cancer Society suggests screening tests, particularly colonoscopy, for early detection of colon cancer. Colonoscopy is the best method, because it will visualize the entire colon and can remove polyps during the procedure. Other screening tests include fecal occult blood tests (annually), stool DNA testing, flexible sigmoidoscopy (every 5 years), and CT
colonography (every 5 years).
These frequency recommendations depend, however, on a person's particular risk of colon cancer due to other risk factors.
In general, physicians recommend standard preventive measures such as keeping a healthy weight, exercising, and increasing consumption of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains while decreasing saturated fat and red meat intake. In addition, people are recommended to limit alcohol consumption and quit smoking
Source:medicalnewstoday.com
Liquid Nano Curcumin OIC is available in large pharmacies in Vietnam. Please contact our Customer Service Hotline at 1900636913 or access DISTRIBUTION CHANNELS to receive information of the nearest pharmacy.
The product is not a medicine and cannot replace medicines
The most-read articles
- HEALTHCARE AND THE USE OF NANOTECHNOLOGY IN MEDICAL APPLICATIONS
- HOME REMEDIES FOR A STOMACH ULCER
- GALLBLADDER DISEASE
- TRY TURMERIC FOR QUICK RELIEF FROM A SORE THROAT
- Pycnogenol
- THE BEST THINGS TO KNOW ABOUT THE ALOE VERA PLANT
- RESULTS OF SCIENTIFIC RESEARCH ON LIQUID NANO CURCUMIN OIC
- NANOTECHNOLOGY IN COSMETICS
- OESOPHAGEAL CANCER
- GOUT: SYMPTOMS, CAUSES, AND TREATMENT
Send your question